- Articles
DNS Security | Protecting Your Business from Cyber Threats
- Articles
DNS Security | Protecting Your Business from Cyber Threats
- Articles
- March 14, 2025
What Is DNS Security?
The Domain Name System (DNS) acts as the internet’s directory, translating user-friendly domain names (e.g., example.com) into numerical IP addresses. DNS security encompasses the protocols, tools, and practices designed to protect this critical system from cyberattacks. By securing DNS infrastructure, organizations ensure uninterrupted connectivity, prevent data breaches, and maintain user trust.
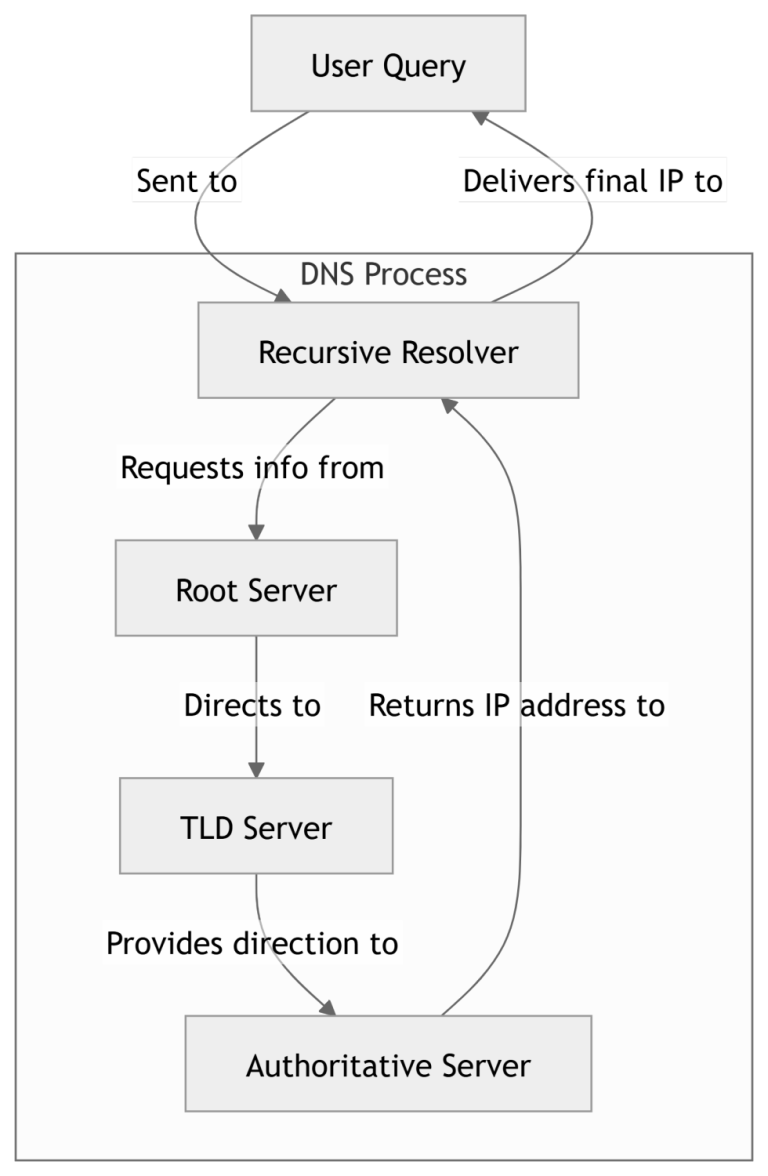
How Does DNS Work?
DNS operates through a hierarchical network of servers:
- Recursive Resolver: Handles user queries and communicates with other DNS servers.
- Root Server: Directs resolvers to Top-Level Domain (TLD) servers (e.g., .com, .net).
- Authoritative Server: Provides the final IP address linked to the requested domain.
While this process is efficient, its decentralized nature makes it vulnerable to exploitation
Why Is DNS Security Critical for Businesses?
- Prevents Malicious Redirection: Blocks access to phishing or fraudulent websites.
- Mitigates Downtime: Protects against attacks like DDoS that disrupt services.
- Stops Data Exfiltration: Detects and blocks DNS tunneling used to leak sensitive data.
- Ensures Compliance: Helps meet regulations like GDPR by safeguarding user privacy.
A compromised DNS can lead to financial losses, legal repercussions, and reputational harm.
4 Common DNS Attacks and Mitigation Strategies
1. DoS/DDoS and DNS Amplification
- Attack Method: Overwhelms servers with fake requests or exploits open resolvers to amplify traffic.
- Prevention: Use traffic filtering, rate limiting, and deploy Anycast DNS for load distribution.
2. DNS Spoofing (Cache Poisoning)
- Attack Method: Injects false DNS records to redirect users to malicious sites.
- Prevention: Implement DNSSEC to authenticate DNS responses.
3. DNS Tunneling
- Attack Method: Uses DNS queries to bypass security controls and exfiltrate data.
- Prevention: Monitor DNS traffic for anomalies and block suspicious domains.
4. DNS Hijacking
- Attack Method: Alters DNS settings to redirect traffic to attacker-controlled servers.
- Prevention: Secure DNS management interfaces with multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Core DNS Security Solutions
1. DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions)
Adds cryptographic signatures to DNS records to verify authenticity and prevent tampering.
2. DNS Filtering
Leverages threat intelligence to block access to malicious or high-risk domains.
3. Advanced Firewalls
Inspect and filter DNS traffic to detect anomalies and enforce security policies.
4. Redundant DNS Architecture
Deploy primary and secondary servers to ensure high availability during attacks.
DNS Security Best Practices
- Enable Detailed Logging: Track DNS queries to identify unusual patterns.
- Secure DNS Caches: Restrict write-access to prevent cache poisoning.
- Filter DNS Traffic: Block requests to known malicious domains.
- Enforce Access Controls: Limit administrative privileges to DNS servers.
- Adopt Zero Trust Principles: Validate all DNS requests, including internal traffic.
DNS, DNSSEC, and DNS Security: Key Differences
- DNS: The foundational system that maps domains to IP addresses.
- DNSSEC: A protocol extension that adds cryptographic authentication to DNS data.
- DNS Security: A comprehensive approach combining DNSSEC, monitoring, and threat prevention.
Emerging DNS Security Trends in 2024
- Healthcare Sector Focus: Protecting IoT medical devices and patient data portals.
- Hybrid Work Challenges: Securing DNS in multi-cloud and remote work environments.
- IoT Whitelisting: Restricting DNS access for connected devices to minimize risks.
- AI-Powered Analytics: Automating threat detection through DNS traffic analysis.
Conclusion
DNS security is vital for maintaining a secure and resilient network. By addressing threats like DDoS, spoofing, and hijacking through solutions such as DNSSEC, traffic filtering, and redundant architectures, businesses can safeguard their digital operations. Adopting best practices like logging, access controls, and Zero Trust principles ensures long-term protection against evolving cyber threats. Prioritizing DNS security is not just a technical necessity—it’s a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategy.
Recent Post
- All Posts
- Articles


